User:Stasconstantine/etrПсиходелики

- (Русский перевод o PsychonautWiki / Russian Translation of PsychonautWiki. Работа в процессе / work in progress.)
Psychedelics are a class of hallucinogens that act primarily by binding to and activating the receptors for serotonin, a key signaling molecule in the brain. Serotonin plays a number of critical roles all throughout the human body but in the brain, it is especially linked to the proper functioning and regulation of sensory perception, behavior, mood, cognition and memory.[1]
Психоде́лики (от греч. ψυχή — «душа», «психика» и греч. δήλος — «ясный», «очевидный») — класс психоактивных веществ, изменяющих восприятие,влияющих на эмоциональное состояние и многие психические процессы, которые действуют путем связывания и активации рецепторов серотонина, ключевой сигнальной молекулы в Центральной Нервной Системе. Серотонин играет множество главных ролей в нервной системе, но в мозге, он особенно связан с функцией и регуляцией чувствительного восприятия, поведения, настроения, познания и памяти.[1]
The term was coined by the British psychiatrist Humphrey Osmond in 1956 and derives from the Greek words ψυχή (psyche, "soul, mind") and δηλείν (delein, "to manifest") which taken together mean "soul-manifesting," with the implication being that psychedelics can allow one to access the soul and develop unused potentials of the human mind.[2][3]
Этот термин был придуман британским психиатром Хамфри Осмондом в 1956 году и был получен путём сложения греческих слов «ψυχή» (psyche, «душа, разум») и «δηλείν» (delein, «проявить, показать»), которые в совокупности означают «проявление души». То есть психоделики могут позволить человеку получить доступ к душе и развить неиспользуемые потенциалы человеческого разума [4][5]
In modern times, psychedelic substances are used in a range of contexts spanning from the shamanic, religious and "spiritual", or the transpersonal. They are often referred to as entheogens ("generating the divine within")[6] by those who use them for these purposes, although they are also used solely for recreational purposes as well.
В наше время психоделические вещества используются в различных контекстах, охватывающих шаманские, религиозные и «духовные», или трансперсональные. Они часто упоминаются как энтеогены («порождение божественного внутри»)[7] теми, кто использует их для этих целей, хотя они также используются исключительно для рекреационных целей.
Способ действия
Psychedelics act on serotonin receptors (also referred to as 5-HT receptors) via the way in which they act as full or partial agonists through their structural similarity to the serotonin molecule. DMT, for example, works by simply fitting into and activating serotonin receptors. It has a higher affinity than serotonin itself for the receptors, therefore preventing serotonin from binding to the receptors by competing with it.
While the method of action behind psychedelics is not fully understood, serotonergic psychedelics are known to show affinities for various 5-HT receptors in different ways and levels and may be classified by their activity at different 5-HT subsites, such as 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A, etc. Many serotonergic psychedelics (such as the tryptamines) share very close chemical and structural similarities to serotonin itself which is thought to account for the range of affinities to 5-HT sites that it displays. It is almost unanimously agreed that serotonergic psychedelics produce their effects by acting as uniquely effective partial agonists at 5-HT2A receptor sites.[11]
Эффекты
Disclaimer: The effects listed below cite the Subjective Effect Index (SEI), an open research literature based on anecdotal user reports and the personal analyses of PsychonautWiki contributors. As a result, they should be viewed with a healthy degree of skepticism.
It is also worth noting that these effects will not necessarily occur in a predictable or reliable manner, although higher doses are more liable to induce the full spectrum of effects. Likewise, adverse effects become increasingly likely with higher doses and may include addiction, severe injury, or death ☠.
Эффекты, перечисленные ниже, основаны на индексе субъективных эффектов и личном опыте авторов PsychonautWiki. Перечисленные эффекты следует принимать с скептикой и редко (или вообще когда-либо) происходят все сразу, но более высокие дозы увеличивают шансы проявления более полного спектра эффектов. Также, побочные эффекты становятся гораздо более вероятными при более высоких дозах, включая даже травму или смерть.
Влияния на зрение 
-
Улучшения
-
Искажения
-
Геометрия
-
Галлюцинаторные состояния
Cognitive effects 
-
Улучшения
- Analysis enhancement
- Emotionality enhancement
- Catharsis
- Creativity enhancement
- Dream potentiation
- Empathy, affection, and sociability enhancement
- Immersion enhancement
- Increased music appreciation
- Increased sense of humor
- Multiple thought streams
- Novelty enhancement
- Personal meaning enhancement
- Rejuvenation
- Thought acceleration
- Thought connectivity
-
Подавления
-
Изменения
-
Transpersonal states
Physical effects 
-
Enhancements
-
Подавление
-
Изменения
-
Неудобные эффекты
Влияния на слух 
Multisensory effects 
Фармакологические группы
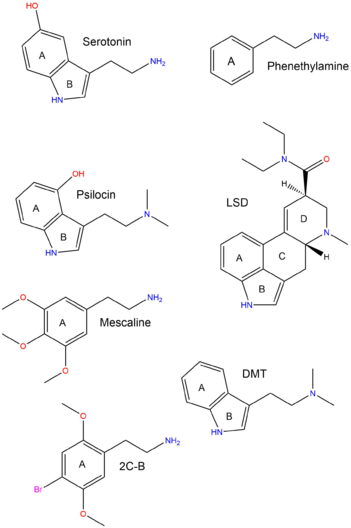
The "classical psychedelics" are all classed as serotonergic in nature.[11]This means that they structurally mimic the endogenous neurotransmitter known as serotonin, the neurotransmitter that regulates higher-level brain functions such as mood, sensory perception, cognition, and memory.[1] The diagram to the right shows the structural similarities and differences between the various classes of psychedelics and the serotonin neurotransmitter. The three classes (phenethylamines, lysergamides and tryptamines) all contain the same chemical rings (which have been labeled).
- A represents the benzene ring, which all three classes contain.
- B represents the pyrrole ring in both tryptamines and lysergamides.
- A and B together form the indole ring.
- C (cyclohexane) and D are only contained in the lysergamides, possibly contributing to their potency.
Examples
Триптамины
-
Производные триптамина
-
Замещенные триптамины
- 4-PO-DMT (Psilocybin)
- 4-HO-DMT (Psilocin)
- 4-HO-MET (Metocin)
- 4-HO-DET (Ethocin)
- 4-HO-MiPT (Miprocin)
- 4-HO-DiPT (Iprocin)
- 4-HO-MPT
- 4-HO-EPT
- 4-HO-DPT
- 4-AcO-DMT (Psilacetin)
- 4-AcO-MET (Metacetin, Azomet)
- 4-AcO-DET (Ethacetin)
- 4-AcO-MiPT (Mipracetin)
- 4-AcO-DiPT (Ipracetin)
- 4-AcO-MPT
- 4-AcO-EPT
- 4-AcO-DPT
- 5-HO-DMT (Bufotenin)
- 5-MeO-DMT
- 5-MeO-MiPT (Moxy)
- 5-MeO-DiPT (Foxy)
- 5-MeO-DALT
- 5-MeO-MALT
Responsible use
The information below describes and explains various concepts regarding the responsible use of psychedelic substances. These should be read over and carefully considered before one decides whether or not the potential benefits of experimenting with psychedelics outweighs the potential risks.
Setting 
- Choosing a suitable place to experience the effects of a hallucinogen is extremely important and plays a major role in determining the outcome of the experience. The ideal place for an inexperienced user is a familiar, safe, indoor environment over which they have full control and is devoid of factors that can negatively influence one's mental state. In order to prepare a proper setting for hallucinogens, it is advised to take the following steps:
-
- Ensure that one is completely free of responsibilities for the duration of the experience, and ideally the day after. This is because even the simplest of tasks can become incredibly difficult and potentially stressful to perform while under the influence of hallucinogens. The user should be prepared to fully relax and not perform chores or everyday routines. This includes driving and operating heavy machinery.
-
- Avoid people who are not directly participating in the experience. This includes relatives who may be sleeping in the same house and friends that are anything but extremely trustworthy, understanding, and informed about the effects of hallucinogens. The mere vicinity of unaware people can prompt anxiety and paranoia as well as prevent full immersion in the experience.
-
- Avoid unfamiliar, loud, cluttered, and/or public environments. The user should select an environment over which they have a considerable degree of control. This can be as simple as having the ability to adjust the air conditioning settings or freely enter and exit a restroom. One should be able to sit, lie down, and walk around as they please for the full duration of the experience. The chosen setting should ideally be equipped with privacy, relaxing music, comfortable seating, and readily available food and water. Examples of such settings include a safe, comfortable room at home or a friend's house.
-
- Avoid sources of anything that can generate "bad vibes." The user should not expose themselves to unpleasant or disturbing stimuli such as scary films or dark music. If bad vibes are encompassing the experience, they can be escaped by quickly changing the immediate environment the user is in. For example, if one is sitting down with the lights off, stand up and turn the lights on, change the music, or move to a different room in the house.
-
- Once the user has become intimately familiar with their substance of choice, it is up to them as an individual whether they would be comfortable tripping in a less controlled environment such as out in nature, social gatherings, parties, raves, etc. However, it should be noted that tripping in these settings entails considerably more physical and legal risk.
Set (State of mind) 
-
The user's set or state of mind in plays a major role in determining the outcome of a trip. Hallucinogens amplify one's current state of mind, mood and outlook: a positive mindset will likely become more positive and a negative one will become even more negative. As a result, hallucinogens should generally be avoided during acutely stressful or negative periods of life. Users should be fully aware of the ways in which hallucinogens, particularly psychedelics, are able to force one to face their internal problems that they may not be psychologically prepared to handle at that time.
Those with preexisting mental conditions (especially individuals with psychotic illnesses like schizophrenia) should avoid hallucinogens due to the way they can strongly amplify one's underlying mental and emotional state as well as promote delusions and hallucinations. Those who wish to take hallucinogens with such conditions should seek the advice of a qualified medical practitioner.
A common piece of advice while tripping is to "let go" and allow the effects of the substance to take charge. One should take the metaphorical passenger seat and forgo trying to control or suppress any part of the experience. It is extremely important that the user simply relaxes and take things as they come, as any resistance will only serve to amplify what is trying to be avoided.
Additionally, the user must understand that the experience of tripping is often ungraspable, meaning that one should accept being unable to understand or express the full scope of what is happening during the experience. The user should embrace the fact that their thought processes, although potentially more lucid in some ways, will be unavoidably impaired along with fine motor control, conversational skills, and situational awareness. The user should be sure to frequently remind themselves that these effects are normal and, most importantly, temporary.
Bodily state 
-
The user's current bodily condition is just as important as one's mood and mindset when going into a trip. If one feels tired, sick or injured, these sensations will manifest as amplified versions of the same conditions which, when combined with possible body load, may easily detract from or ruin the experience.
Instead of tripping while stressed, tired, sick or injured, one should wait for a more suitable opportunity. This will drastically lower the chances of having a negative or unfulfilling experience.
Trip sitters 
-
Main article: Trip sitter When using hallucinogens, a trip sitter is strongly recommended to be present, particularly if one is inexperienced with the substance. It is the trip sitter's responsibility to assist the individual or group by maintaining a calm and grounded frame of mind. This can be accomplished by simply watching over the trippers and calmly reassuring them if they experience any anxiety or stress, while also preventing them from coming to any harm. There is an obvious correlation between the name "trip sitter" and "baby sitter": this is because trip sitting often feels like babysitting and it is a responsibility that must be taken every bit as seriously.
A good trip sitter must fulfill a number of requirements. In addition to being a generally responsible adult, they should ideally be sober and able to relate to the group members' situation from either personal experiences or researched knowledge. Trip sitters should understand that when an individual is tripping, they may not be able to communicate or interact as they usually do. Also, their balance and spatial judgment may be impaired so assistance in performing tasks such as staying hydrated or navigating through an area can greatly reduce anxiety and confusion. The trip sitter can participate in the conversation, but should also remember to give the trippers space to explore the experience without too much external influence.
Once the user becomes familiar with a substance, it becomes a personal choice as to whether or not they feel comfortable enough to trip without a sitter. It is also advised to use trip sitters when taking high doses or a dose one has never taken before. It should be remembered that having friends around while tripping is the best way to avoid potential psychological, medical, or legal consequences.
Anchors 
-
 "You are tripping on 2C-P" - This sign is an example of an anchor which can be used to keep one grounded during ego death.
"You are tripping on 2C-P" - This sign is an example of an anchor which can be used to keep one grounded during ego death.In the context of hallucinogen use, an anchor is an activity or physical object which keeps the user grounded during the heavy distortion of a person's sense of time, space, memory, and sense of self. At higher dosages, this can result in extreme disorientation and confusion. Anchors are often used to counteract this and maintain one's concept of the current situation as it is within reality.
Examples of anchors include:
-
- Familiar and uplifting music. An example of this includes our community good vibes portal. However, users are encouraged to create their own playlist that is composed of music one personally associates with being happy and relaxed.
-
- An extremely personal and ingrained image or object.
-
- Continuous repetition of a meaningful word or motto as a mantra.
-
- Writing an easily readable reminder onto a large piece of paper and placing it close within one's visual field throughout the experience. Common reminders include the name of the substance along with its dosage and phrases such as "You are tripping on LSD." The same principle can be used to write reminders on one's hand or other visible body parts.
-
- An item of clothing or an accessory that is only worn during and therefore associated with the act of tripping.
Aborting trips 
-
Hallucinogens have the potential to become overwhelming and push the user into a paranoid or dreadful mood, particularly if they are inexperienced or in an inappropriate set and setting.
If one decides to terminate the trip, benzodiazepines and other sedatives such as some antipsychotics can be considered analogous to an "eject button" of a downhill-headed or extensively long trip. These substances tend to be very effective tools in preventing panic attacks, paranoia, and possible traumatic experiences.However, experienced users generally advise trying to wait out difficult parts of a trip if possible. Challenging moments are often temporary and can turn out to be catalysts for the greatest learning experiences.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Nichols, D. E., & Nichols, C. D. (2008). Serotonin Receptors. Chemical Reviews, 108(5), 1614-1641. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr078224o
- ↑ A. Weil, W. Rosen. (1993), From Chocolate To Morphine: Everything You Need To Know About Mind-Altering Drugs.New York, Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 93
- ↑ Erowid. (1998, August 9). Erowid Humphry Osmond Vault. Retrieved from https://erowid.org/culture/characters/osmond_humphry/osmond_humphry.shtml
- ↑ A. Weil, W. Rosen. (1993), From Chocolate To Morphine: Everything You Need To Know About Mind-Altering Drugs.New York, Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 93
- ↑ Erowid. (1998, August 9). Erowid Humphry Osmond Vault. Retrieved from https://erowid.org/culture/characters/osmond_humphry/osmond_humphry.shtml
- ↑ Dictionary - Entheogen | http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/entheogen
- ↑ Dictionary - Entheogen | http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/entheogen
- ↑ Petri, G., Expert, P., Turkheimer, F., Nutt, D., Hellyer, P. J., & Vaccarino, F. (2014). Homological scaffolds of brain functional networks, 14–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2618
- ↑ Carhart-Harris, R. L., Muthukumaraswamy, S., Roseman, L., Kaelen, M., Droog, W., Murphy, K., … Nutt, D. J. (2016). Neural correlates of the LSD experience revealed by multimodal neuroimaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518377113
- ↑ Vollenweider, F. X., & Kometer, M. (2010). The Neurobiology of Psychedelic Drugs: Implications for the Treatment of Mood Disorders. Nature Publishing Group, 11(9), 642–651. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2884
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Nichols, D. E. (2016). Psychedelics. Pharmacological Reviews, 68(2), 264-355. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.115.011478
- ↑ Psychedelics: entering a new age of addiction therapy | http://www.pharmaceutical-journal.com/news-and-analysis/features/psychedelics-entering-a-new-age-of-addiction-therapy/20066899.article#fn_link_1