Clonazepam

Fatal overdose may occur when benzodiazepines are combined with other depressants such as opiates, barbiturates, gabapentinoids, thienodiazepines, alcohol or other GABAergic substances.[1]
It is strongly discouraged to combine these substances, particularly in common to heavy doses.
| Summary sheet: Clonazepam |
| Clonazepam | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Nomenclature | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common names | Clonazepam, Klonopin, K-Pins, Rivotril | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substitutive name | Clonazepam | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Systematic name | 5-(2-Chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class Membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychoactive class | Depressant | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical class | Benzodiazepine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Routes of Administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stimulants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depressants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dissociatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clonazepam[3] (trade name Klonopin or Rivotril) is a long-acting psychoactive substance of the benzodiazepine class which produces mainly anxiolytic, but also anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, amnesic, sedative, depressant and hypnotic effects.[4] It is commonly used and FDA approved for the medical treatment of panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), and social anxiety disorder (SAD). In Europe, it is generally approved for treatment-resistent epilepsy.
Clonazepam has an elimination half-life of 30 – 40 hours[5], and is considered to be a long-acting benzodiazepine. Clonazepam has rapid onset of action, with a peak blood level occurring one to four hours after oral administration.
It's worth noting that the sudden discontinuation of benzodiazepines can be potentially life-threatening for individuals using regularly for extended periods of time.[6] It is highly recommended to taper one's dose by gradually lowering the amount taken each day for a prolonged period of time instead of stopping abruptly.[7] Not doing so can lead to serious health problems and even death.
Chemistry
Clonazepam is a drug of the benzodiazepine class. Benzodiazepine drugs contain a benzene ring fused to a diazepine ring, which is a seven membered ring with the two nitrogen constituents located at R1 and R4. The benzyl ring of clonazepam is substituted at R8 with a nitro group, NO2-. Further, the diazepine ring is bonded at R5 to a 2-chlorinated phenyl ring. Clonazepam also contains an oxygen group double bonded to R2 of its diazepine ring to form a ketone. This oxygen substitution at R2 is shared with other benzodiazepine drugs with the suffix -azepam.
Pharmacology
Benzodiazepines produce a variety of effects by binding to the benzodiazepine receptor site and magnifying the efficiency and effects of the neurotransmitter gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) by acting on its receptors.[8] As this site is the most prolific inhibitory receptor set within the brain, its modulation results in the sedating (or calming effects) of clonazepam on the nervous system.
The anticonvulsant properties of benzodiazepines may be, in part or entirely, due to binding to voltage-dependent sodium channels rather than benzodiazepine receptors.[9]
Subjective effects
Disclaimer: The effects listed below cite the Subjective Effect Index (SEI), an open research literature based on anecdotal user reports and the personal analyses of PsychonautWiki contributors. As a result, they should be viewed with a healthy degree of skepticism.
It is also worth noting that these effects will not necessarily occur in a predictable or reliable manner, although higher doses are more liable to induce the full spectrum of effects. Likewise, adverse effects become increasingly likely with higher doses and may include addiction, severe injury, or death ☠.
Physical effects 
-
- Sedation - In terms of energy level alterations, this drug has the potential to be extremely sedating and often results in an overwhelmingly lethargic state. At higher levels, this causes users to suddenly feel as if they are extremely sleep deprived and have not slept for days, forcing them to sit down and generally feel as if they are constantly on the verge of passing out instead of engaging in physical activities. This sense of sleep deprivation increases proportional to dosage and eventually becomes powerful enough to force a person into complete unconsciousness.
- Dizziness
- Muscle relaxation - This effect is relatively strong when compared with alprazolam.
- Motor control loss
- Respiratory depression
- Seizure suppression
- Physical euphoria - Clonazepam is similar to alprazolam, where despite suppressing emotion, people report moderate-strong feelings of relaxation, pleasure and comfort in the body. This seems to present itself more often in those with pre-existing anxiety. However, this isn't consistent with everyone, with some users reporting no euphoric qualities at all.
Visual effects 
-
- Visual acuity suppression - Like many depressants, clonazepam is known to cause blurred or otherwise suppressed visual acuity.
Paradoxical effects 
- Paradoxical reactions to benzodiazepines such as increased seizures (in epileptics), aggression, increased anxiety, violent behavior, loss of impulse control, irritability and suicidal behavior sometimes occur (although they are rare in the general population, with an incidence rate below 1%).[10][11] These paradoxical effects occur with greater frequency in recreational abusers, individuals with mental disorders, children, and patients on high-dosage regimes.[12]
Cognitive effects 
-
The cognitive effects of clonazepam can be broken down into several components which progressively intensify proportional to dosage. The general head space of clonazepam is described by many as one of intense relaxation, anxiety suppression and decreased inhibition. It contains a large number of typical depressants cognitive effects.
The most prominent of these cognitive effects generally include:
- Amnesia
- Anxiety suppression
- Thought deceleration
- Analysis suppression
- Delusions of sobriety - This is the false belief that one is perfectly sober despite obvious evidence to the contrary such as severe cognitive impairment and an inability to fully communicate with others. It most commonly occurs at heavy dosages.
- Disinhibition
- Compulsive redosing
- Emotion suppression - Although this compound primarily suppresses anxiety, it also dulls other emotions in a manner which is distinct but less intensive than that of antipsychotics.
- Dream potentiation
After effects 
-
- Rebound anxiety - Rebound anxiety is a commonly observed effect with anxiety relieving substances like benzodiazepines. It typically corresponds to the total duration spent under the substance's influence along with the total amount consumed in a given period, an effect which can easily lend itself to cycles of dependence and addiction.
- Dream potentiation[13] or Dream suppression
- Residual sleepiness - While benzodiazepines can be used as an effective sleep-inducing aid, their effects may persist into the morning afterward, which may lead users to feeling "groggy" or "dull" for up to a few hours.
- Thought deceleration
- Thought disorganization
- Irritability
Experience reports
Anecdotal reports which describe the effects of this compound within our experience index include:
- Experience:4mg clonazepam - Notes
- Experience:A combination of tramadol, clonazepam, gabapentin, and dimenhydrinate
Additional experience reports can be found here:
Toxicity and harm potential
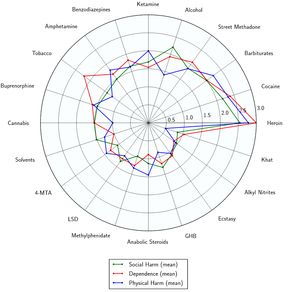
Clonazepam has a low toxicity relative to dose.[15] However, it is potentially lethal when mixed with depressants like alcohol or opioids.
It is strongly recommended that one use harm reduction practices when using this drug.
Tolerance and addiction potential
Clonazepam is extremely physically and psychologically addictive.
Tolerance will develop to the sedative-hypnotic effects within a couple of days of continuous use. After cessation, the tolerance returns to baseline in 7 - 14 days. However, in certain cases this may take significantly longer in a manner which is proportional to the duration and intensity of one's long-term usage.
Withdrawal symptoms or rebound symptoms may occur after ceasing usage abruptly following a few weeks or longer of steady dosing, and may necessitate a gradual dose reduction. For more information on tapering from benzodiazepines in a controlled manner, please see this guide.
Benzodiazepine discontinuation is notoriously difficult; it is potentially life-threatening for individuals using regularly to discontinue use without tapering their dose over a period of weeks. There is an increased risk of hypertension, seizures, and death.[6] Drugs which lower the seizure threshold such as tramadol should be avoided during withdrawal.
Clonazepam presents cross-tolerance with all benzodiazepines, meaning that after its consumption all benzodiazepines will have a reduced effect.
Overdose
Benzodiazepine overdose may occur when a benzodiazepine is taken in extremely heavy quantities or concurrently with other depressants. This is particularly dangerous with other GABAergic depressants such as barbiturates and alcohol since they work in a similar fashion, but bind to distinct allosteric sites on the GABAA receptor, thus their effects potentiate one another. Benzodiazepines increase the frequency in which the chlorine ion pore opens on the GABAA receptor while barbiturates increase the duration in which they are open, meaning when both are consumed, the ion pore will open more frequently and stay open longer[16]. Benzodiazepine overdose is a medical emergency that may lead to a coma, permanent brain injury or death if not treated promptly and properly.
Symptoms of a benzodiazepine overdose may include severe thought deceleration, slurred speech, confusion, delusions, respiratory depression, coma or death. Benzodiazepine overdoses may be treated effectively in a hospital environment, with generally favorable outcomes. Benzodiazepine overdoses are sometimes treated with flumazenil, a GABAA antagonist[17], however care is primarily supportive in nature.
Dangerous interactions
Warning: Many psychoactive substances that are reasonably safe to use on their own can suddenly become dangerous and even life-threatening when combined with certain other substances. The following list provides some known dangerous interactions (although it is not guaranteed to include all of them).
Always conduct independent research (e.g. Google, DuckDuckGo, PubMed) to ensure that a combination of two or more substances is safe to consume. Some of the listed interactions have been sourced from TripSit.
- Depressants (1,4-Butanediol, 2M2B, alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, GHB/GBL, methaqualone, opioids) - This combination potentiates the muscle relaxation, amnesia, sedation, and respiratory depression caused by one another. At higher doses, it can lead to a sudden, unexpected loss of consciousness along with a dangerous amount of depressed respiration. There is also an increased risk of suffocating on one's vomit while unconscious. If nausea or vomiting occurs before a loss of consciousness, users should attempt to fall asleep in the recovery position or have a friend move them into it.
- Dissociatives - This combination can unpredictably potentiate the amnesia, sedation, motor control loss and delusions that can be caused by each other. It may also result in a sudden loss of consciousness accompanied by a dangerous degree of respiratory depression. If nausea or vomiting occurs before consciousness is lost, users should attempt to fall asleep in the recovery position or have a friend move them into it.
- Stimulants - Stimulants mask the sedative effect of depressants, which is the main factor most people use to gauge their level of intoxication. Once the stimulant effects wear off, the effects of the depressant will significantly increase, leading to intensified disinhibition, motor control loss, and dangerous black-out states. This combination can also potentially result in severe dehydration if one's fluid intake is not closely monitored. If choosing to combine these substances, one should strictly limit themselves to a pre-set schedule of dosing only a certain amount per hour until a maximum threshold has been reached.
Legal status
Internationally, clonazepam is included under the United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances in Schedule IV.[18]
- Australia: Clonazepam is available by prescription only.[citation needed]
- Brazil: Clonazepam is a "black stripe" drug, which are available by prescription only.[19]
- Canada: Clonazepam is a Schedule IV drug.[citation needed]
- Czech Republic: Clonazepam is a Schedule IV [20] (List 7) substance. Sold exclusively by prescription "without a blue stripe" (§ 1, g), 2. of Nařízení vlády č. 463/2013 Sb.). [21]
- Germany: Clonazepam is controlled under Anlage III BtMG (Narcotics Act, Schedule III) as of August 1, 1986.[22] It can only be prescribed on a narcotic prescription form, except preparations which contain up to 2 mg clonazepam in each dosage form and solutions that contain up to 0.25% and under 250 mg clonazepam in total per packaging unit.[23]
- India: Clonazepam is Schedule H in India.[citation needed]
- Israel: Clonazepam is available by prescription only.[citation needed]
- New Zeland: Clonazepam is a Schedule 3 controlled drug.[24]
- Norway: Clonazepam is available by prescription only.[25]
- Russia: Clonazepam is a Schedule III controlled substance as of April 2013.[26]
- Switzerland: Clonazepam is a controlled substance specifically named under Verzeichnis B. Medicinal use is permitted.[27]
- Turkey: Clonazepam is a 'green prescription' only substance[28] and illegal when sold or possessed without a prescription.[citation needed]
- United Kingdom: Clonazepam is a Class C drug. [29]
- United States: Clonazepam is a Schedule IV substance.[citation needed]
See also
External links
- Clonazepam (Wikipedia)
- Clonazepam (Erowid Vault)
- Clonazepam (Isomer Design)
- Clonazepam (DrugBank)
- Clonazepam (Drugs.com)
References
- ↑ Risks of Combining Depressants - TripSit
- ↑ FDA Approved Labeling Text (October 2013) (PDF)
- ↑ Patent US3123529 (PDF)
- ↑ Cowen, P. J., Green, A. R., Nutt, D. J. (5 March 1981). "Ethyl beta-carboline carboxylate lowers seizure threshold and antagonizes flurazepam-induced sedation in rats". Nature. 290 (5801): 54–55. doi:10.1038/290054a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
- ↑ Basit H, Kahwaji CI. Clonazepam. [Updated 2022 Sep 1]. In: StatPearls [1]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lann, M. A., Molina, D. K. (June 2009). "A fatal case of benzodiazepine withdrawal". The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 30 (2): 177–179. doi:10.1097/PAF.0b013e3181875aa0. ISSN 1533-404X.
- ↑ Kahan, M., Mailis-Gagnon, A., Tunks, E. (June 2011). "Canadian guideline for safe and effective use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: implications for pain physicians". Pain Research & Management. 16 (3): 157–158. doi:10.1155/2011/434298. ISSN 1203-6765.
- ↑ Haefely, W. (29 June 1984). "Benzodiazepine interactions with GABA receptors". Neuroscience Letters. 47 (3): 201–206. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(84)90514-7. ISSN 0304-3940.
- ↑ McLean, M. J., Macdonald, R. L. (February 1988). "Benzodiazepines, but not beta carbolines, limit high frequency repetitive firing of action potentials of spinal cord neurons in cell culture". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 244 (2): 789–795. ISSN 0022-3565.
- ↑ Saïas, T., Gallarda, T. (September 2008). "[Paradoxical aggressive reactions to benzodiazepine use: a review]". L’Encephale. 34 (4): 330–336. doi:10.1016/j.encep.2007.05.005. ISSN 0013-7006.
- ↑ Paton, C. (December 2002). "Benzodiazepines and disinhibition: a review". Psychiatric Bulletin. 26 (12): 460–462. doi:10.1192/pb.26.12.460. ISSN 0955-6036.
- ↑ Bond, A. J. (1 January 1998). "Drug- Induced Behavioural Disinhibition". CNS Drugs. 9 (1): 41–57. doi:10.2165/00023210-199809010-00005. ISSN 1179-1934.
- ↑ Goyal, S. (14 March 1970). "Drugs and dreams". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 102 (5): 524. ISSN 0008-4409.
- ↑ Nutt, D., King, L. A., Saulsbury, W., Blakemore, C. (24 March 2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse". The Lancet. 369 (9566): 1047–1053. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60464-4. ISSN 0140-6736.
- ↑ Mandrioli, R., Mercolini, L., Raggi, M. A. "Benzodiazepine Metabolism: An Analytical Perspective". Current Drug Metabolism. 9 (8): 827–844.
- ↑ Twyman, R. E., Rogers, C. J., Macdonald, R. L. (March 1989). "Differential regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor channels by diazepam and phenobarbital". Annals of Neurology. 25 (3): 213–220. doi:10.1002/ana.410250302. ISSN 0364-5134.
- ↑ Hoffman, E. J., Warren, E. W. (September 1993). "Flumazenil: a benzodiazepine antagonist". Clinical Pharmacy. 12 (9): 641–656; quiz 699–701. ISSN 0278-2677.
- ↑ "List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control" (PDF). International Narcotics Control Board. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 19, 2013. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- ↑ Anvisa
- ↑ https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:6b5e9beb-1d9b-11ea-95ab-01aa75ed71a1.0001.02/DOC_1&format=PDF
- ↑ https://www.zakonyprolidi.cz/cs/2013-463
- ↑ "Zweite Verordnung zur Änderung betäubungsmittelrechtlicher Vorschriften" (PDF) (in German). Bundesanzeiger Verlag. Retrieved December 26, 2019.
- ↑ "Anlage III BtMG" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz. Retrieved December 26, 2019.
- ↑ Misuse of Drugs Act 1975 No 116 (as at 01 July 2022), Public Act Schedule 3 Class C controlled drugs – New Zealand Legislation
- ↑ https://www.felleskatalogen.no/medisin/rivotril-roche-563568
- ↑ Постановление Правительства РФ от 04.02.2013 N 78 “О внесении изменений в некоторые акты Правительства Российской Федерации” - КонсультантПлюс
- ↑ "Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien" (in German). Bundeskanzlei [Federal Chancellery of Switzerland]. Retrieved January 1, 2020.
- ↑ YEŞİL REÇETEYE TABİ İLAÇLAR | https://www.titck.gov.tr/storage/Archive/2019/contentFile/01.04.2019%20SKRS%20Ye%C5%9Fil%20Re%C3%A7eteli%20%C4%B0la%C3%A7lar%20Aktif%20SON%20-%20G%C3%9CNCEL_58b1ff4a-2e1c-4867-bad7-eec855d6162a.pdf
- ↑ List of most commonly encountered drugs currently controlled under the misuse of drugs legislation