Talk:Blue Lotus
Nymphaea nouchali var. caerulea (Commonly known as Blue Lotus) is a water lily found throughout most of the eastern half of Africa.
| Blue Lotus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [[ File: | frameless | center | 245px ]] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Nomenclature | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common names | Blue Lotus, Nymphaea nouchali var. caerulea, Lotus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class Membership | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychoactive class | Sedative | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical class | Morphinans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Routes of Administration | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The flower has been used for over 2000 years in teas, herbal blends and in perfumes.
Like other species in the genus, the plant contains the psychoactive alkaloid aporphine which is thought to be the main constituent causing the effects of the flower, however, it is more likely a group of aporphine alkaloids are working in conjunction to create the various effects as opposed to just aporphine. High potent extracts when ingested or smoked in high doses are reported to produce euphoria and hallucinations.
History and culture
Blue Lotus is thought to be the primary for the fruit of the lotus tree eaten by the mythical Lotophagi (Lotus Eaters) in Homer's Odyssey. The Lotus Eaters were a race of people living on an island dominated by the lotus tree, after they ate the lotus, they would forget their home and loved ones and long only to stay with their fellow lotus-eaters, falling into a infinite euphoric stupor. Those who ate the plant never cared to report or return.
This lotus has been used to produce perfumes since egyptian times. According to a 2023 preprint study, traces of Peganum harmala, and Blue Lotus were identified in an Egyptian ritual Bes-vase, of the 2nd century BCE
The plant and flower are very prominent and frequent in Ancient Egyptian art, cuisine and perfumes. Blue Lotus flowers have been depicted in numerous stone carvings and paintings, including the walls of the temple of Karnak, and may be associated with rites pertaining to the afterlife. At Heliopolis, the origin of the world was taught to have been when the sun god Ra emerged from a lotus flower growing in "primordial waters". At night, he was believed to retreat into the flower again.
Chemistry
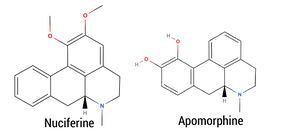
The plant has been found to contain aporphine and similar alkaloids as well as Nuciferine. The effects of Blue Lotus are thought to be down to these compounds but other various Quinoline alkaloids could play a role.
Pharmacology
aporphine, thought to be the main active component, dopamine receptor agonist targeting the D1 and D2 receptors. Nuciferine, also a prominent alkaloid, is an antagonist at 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, and 5-HT2B receptors, but is also a partial agonist at D2, D5, and 5-HT6 receptors, and an agonist at 5-HT1A and D4 receptors. Additionally, it inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT). The group of alkaloids known as Aporphines cause the effects of Blue Lotus. This group contains many Dopamine agonists, a wide range of Serotonin antagonists and Agonists and various reuptake inhibitors. Apomorphine, the active metabolite of Aporphine, has a catechol structure similar to that of dopamine.
Subjective effects
Physical effects 
-
Blue Lotus most potent effects are the sedation and muscle relaxation it causes. This leads many to use it as a sleep aid or lucid dreaming aid.
You may select physical effects to add below here.
- Pain relief- Mild to Moderate pain relief is noted on low to high doses of Blue Lotus. This is thought to be down to the disinhibited and drowsy state it causes.
- Sedation- Sedation is intense on all doses of Blue Lotus and is one of many of the most prominent effects.
- Muscle relaxation- Along with sedation, many report muscle relaxation, a feeling of melting into surroundings.
- Headache- Extremely high doses of Blue Lotus commonly cause Headaches but these can also occur at any dosage depending on the person.
- Nausea- Nausea is common depending on the method of consumption. It is most noted to occur when drunk in a tea or smoked as a resin.
Visual effects 
-
While subtle, if enough is ingested (Most often through smoking), Blue Lotus can cause visual effects and enhancements.
You may select visual effects to add below here.
Enhancements
- Color enhancement - Blue Lotus can have subtle color enhancements, especially when smoked, colors seem to be noticeably more vibrant and enhanced.
Distortions
- Tracers- Minor tracers can appear at any dose and have been reported from low doses as well as high doses. This is most noticed when the head is moved.
- Brightness alteration- In combination with Color enhancement, the scenery is often described as brighter or more vibrant.
- Perspective distortion- In massive doses, many report their environment seeming to grow and shrink behind objects they are focusing on. Changes in body size while lying down are common at all doses.
Cognitive effects 
-
Blue Lotus has most of its cognitive effects manifest themself in sleep. This leads many to use it as a sleep aid or lucid dreaming aid.
You may select from a list of cognitive effects to add below here.
- Increased music appreciation- Music can sound crisp or higher quality, leading to a greater appreciation of music. This effect seems to be potent and pronounced at all dosages, but mostly noticeable when smoked.
- Empathy, affection, and sociability enhancement- Many report the urge to interact or be around others, similar to a drunk feeling. However many also report the sleepiness and drowsiness makes socialising unbearable.
- Dream potentiation- Perhaps the most potent effect of Blue Lotus is the dreams it can bring on. It is most commonly used as a lucid dreaming aid, placing Blue Lotus also into the Oneirogen category.
- Derealization- Many users report a feeling of dissociation to their surroundings or themselves. This is most common when trying to fall asleep.
- Sleepiness- Blue Lotus causes a drowsy sleepy effect at all dosages. This has lead it to become a common sleep aid.
- Disinhibition- Blue Lotus causes an drunk like disinhibition in some, but in others has the opposite effect.
- Focus suppression- It is noticeably hard to concentrate on high doses of Blue Lotus due to the disinhibition and drowsiness it causes.
Auditory effects 
-
Blue Lotus most prominent auditory effect is the enhancement of music. This can be described as the music sounding sharper or more clear.
You may select from a list of auditory effects to add below here.
- Auditory acuity enhancement- Music can sound crisp or higher quality, leading to a greater appreciation of music. This effect seems to be potent and pronounced at all dosages, but mostly noticeable when smoked.
Experience reports
There are currently 0 experience reports describing the effects of this substance in our experience index. You can also submit your own experience report using the same link.
Toxicity and harm potential
The toxicity of Blue Lotus is misunderstood and poorly researched. Only the pure alkaloids have been tested with little toxicity, however, mixing Blue Lotus with other substances could present a risk.
It is strongly recommended that one use harm reduction practices when using this substance.
Lethal dosage
There are no studies on aporphine in animals. However, studies on subcutaneous apomorphine injection, the bioactive form of aporphine, have been carried out. In a 5-day study, mice were administered up to 10 mg/kg apomorphine subcutaneously daily. No adverse effects were observed other than a slight increase in dopamine levels.
Tolerance and addiction potential
Blue Lotus is not thought to be addictive. Its compounds have been used in the treatment of alcohol and morphine addiction.
Dangerous interactions
The main and absolute contraindication to using Blue Lotus, is the concurrent use of adrenergic receptor antagonists; combined, they cause a severe drop in blood pressure and fainting.
L-DOPA and Blue Lotus could pose risks and cause symptoms such as sleepiness, dizziness, runny nose, sweating and tremors. Warning: Many psychoactive substances that are reasonably safe to use on their own can suddenly become dangerous and even life-threatening when combined with certain other substances. The following list provides some known dangerous interactions (although it is not guaranteed to include all of them).
Always conduct independent research (e.g. Google, DuckDuckGo, PubMed) to ensure that a combination of two or more substances is safe to consume. Some of the listed interactions have been sourced from TripSit.
Legal status
Nymphaea caerulea has been illegal in Latvia since November 2009. It is a schedule 1 drug. Possession of large quantities can be punished by up to 15 years in prison.
Nymphaea caerulea was also banned in Poland in March 2009.
Nymphaea caerulea has been illegal in Russia since April 2009.
Nymphaea caerulea is completely prohibited in the state of Louisiana, making it the only state to ban the flower.
Nymphaea caerulea, if sold for human consumption, could fall under the UK's Psychoactive Substances Act 2016, however, this law is rarely imposed on plants and small scale possession.
See also
External links
(List along order below)
Literature
- APA formatted reference
Please see the citation formatting guide if you need assistance properly formatting citations.
References