Talk:Withania somnifera (botany)
This page has not been fully approved by the PsychonautWiki administrators. It may contain incorrect information, particularly with respect to dosage, duration, subjective effects, toxicity and other risks. It may also not meet PW style and grammar standards. |
| Withania somnifera | |
|---|---|
|
An ashwagandha plant found in nature. |
|
| Taxonomical nomenclature | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Unranked | Angiosperms |
| Unranked | Eudicots |
| Unranked | Asterids |
| Order | Solanales |
| Family | Solanaceae |
| Genus | Withania |
| Species | W. somnifera |
| Common nomenclature | |
| Common names | Ashwagandha, Indian ginseng, Poison gooseberry and Winter cherry |
| Constituents | |
| Active constituents | Tropine, withanolides, cuscohygrine |
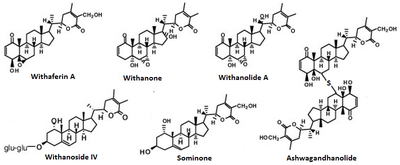
Withania somnifera (Commonly known as Ashwagandha, Indian ginseng, Poison gooseberry and Winter cherry) is an adaptogenic[1] plant in the Solanaceae or Nightshade family that is used as a herbal treatment in Ayurvedic medicine. Ashwagandha contains flavonoids such as Withanolide A and Withaferin-A, which are believed to be responsible for Ashwagandha's psychoactive properties.
Ashwagandha has been well-researched for a multitude of health benefits, including anxiety reduction[2], stress reduction[3], physical performance enhancing[4][5], depression relief[6], and fatigue relief[7].
Chemistry
This chemistry section is incomplete. You can help by adding to it. |
Withanolides are present in all plants in the Solanaceae family of plants[citation needed], of which Withania Somnifera(Ashwagandha) is the highest in concentrations. These Withanolides are believed to be the prime component of Ashwagandha's psychoactive profile.[8]There has been reported to be high variability in the amount of active withanolides in common nutritional supplements, which may be due to lack of standardization of root powder.
Pharmacology
Subjective effects
The effects listed below are based upon the subjective effect index and personal experiences of PsychonautWiki contributors. The listed effects will rarely (if ever) occur all at once, but heavier dosages will increase the chances and are more likely to induce a full range of effects.
Physical effects
- Sedation and Stimulation - Ashwagandha has sedating as well as stimulating effects on the user at all dosages.
- Muscle relaxation - at heavy doses, ashwagandha induces light muscle relaxation.
Cognitive effects
- Anxiety suppression - Ashwagandha produces anxiolytic effects which are comparable to a mild dose of a benzodiazepine but without the accompanying disinhibition.
- Depression reduction
- Motivation enhancement
- Thought deceleration
- Thought organization
- Analysis enhancement
- Focus enhancement
- Perception of increased weight
Experience reports
There are currently no anecdotal reports which describe the effects of this compound within our experience index. Additional experience reports can be found here:
Toxicity and harm potential
It is strongly recommended that one use harm reduction practices when using this drug.
Tolerance and addiction potential
Ashwaghanda is not habit-forming.
Legal issues
 |
This legality section is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
See also
External links
References
- ↑ Withania somnifera: an Indian ginseng. |http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17959291
- ↑ Naturopathic care for anxiety: a randomized controlled trial ISRCTN78958974. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19718255
- ↑ A prospective, randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23439798
- ↑ Effects of Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha) and Terminalia arjuna (Arjuna) on physical performance and cardiorespiratory endurance in healthy young adults. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21170205
- ↑ Examining the effect of Withania somnifera supplementation on muscle strength and recovery: a randomized controlled trial.| http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26609282
- ↑ A double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of the anxiolytic efficacy of an ethanolic extract of withania somnifera. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21407960
- ↑ Naturopathic care for anxiety: a randomized controlled trial ISRCTN78958974. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19718255
- ↑ A standardized root extract of Withania somnifera and its major constituent withanolide-A elicit humoral and cell-mediated immune responses by up regulation of Th1-dominant polarization in BALB/c mice. | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17336338